Key Findings
- The Section 232 tariffs on imports of steel and aluminum raised the cost of production for manufacturers, reducing employment in those industries, raising prices for consumers, and hurting exports.
- The jobs “saved” in the steel-producing industries from the tariffs came at a high cost to consumers, at roughly $650,000 per job saved according to the Peterson Institute for International Economics.
- According to Tax Foundation estimates, repealing the Section 232 tariffs would increase long-run GDP by 0.02 percent and create more than 4,000 jobs.
- Other estimates, such as those from economists Lydia Cox and Kadee Russ, suggest that job losses from the tariffs were as high as 75,000.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Economists have long recognized that tariffs on imports of intermediate inputs (i.e., goods that are used in the production process) can have a negative impact on the economy. While these tariffs may benefit producers of those intermediate inputs and stimulate employment in those protected industries, they often come at a high cost to other industries in the economy. Ultimately, the costs of these tariffs are borne by consumers, who face higher prices for goods that use the tariffed inputs.
The Section 232 tariffs on steel and aluminum, enacted in 2018 under the Trump administration and continued under the Biden administration, fall into this camp of harmful economic policies. This paper provides an overview of Section 232 tariffs on steel and aluminum and shows how they have harmed the U.S. economy. Using the Tax Foundation’s General Equilibrium Model, we estimate that repealing the tariffs would boost long-run GDP and create thousands of jobs.
Background
Under Section 232 of the Trade Expansion Act of 1962, the President may impose tariffs if “an article is being imported in the United States in such quantities or under such circumstances as to threaten or impair the national security.” Since it began, the Department of Commerce (DOC) has authorized 31 trade investigations, ruling in about half of the cases that the imports in question threatened national security.[1] Nonetheless, in several of these cases the President did not take any action and the remedies were rarely tariffs. Prior to the Trump administration, the last presidential action under Section 232 occurred in 1986, when President Reagan signed voluntary export restraint agreements with trading partners regarding imports of metal-cutting and metal-forming machine tools.[2]
In 2017, President Trump asked the DOC to investigate alleged national security threats regarding imports of steel and aluminum. Notably, the DOC adopted a broader definition of national security to include the “general security and welfare of certain industries, beyond those necessary to satisfy national defense requirements,” in contrast to an earlier investigation initiated in 2001 under the Bush administration. The 2017 investigation generated nearly 300 comments, with domestic steel and aluminum producers supporting actions to reduce imports and producers in steel- and aluminum-consuming industries opposing them.[3]
The DOC concluded its investigation in early 2018, recommending that imports be reduced “to a level that should…enable U.S. steel mills to operate 80 percent or more of their rated production capacity.”[4] Following this, President Trump imposed 25 percent tariffs on $16 billion worth of imported steel and 10 percent tariffs on $9 billion worth of imported aluminum in March 2018. Several U.S. trading partners filed complaints with the World Trade Organization, arguing that the tariffs violated long-standing commitments as part of the General Agreement on Trade and Tariffs (GATT).[5] Canada, Mexico, China, the EU, India, Russia, and Turkey responded with retaliatory tariffs against U.S. exports.
Certain exemptions and exclusions were granted for particular countries. Australia was entirely exempt from the tariffs. South Korea, Brazil, and Argentina agreed to a steel quota, but all three were still subject to the aluminum tariffs. The U.S., Canada, and Mexico eventually agreed to lift tariffs on each other following the signing of the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), which included new rules of origin for automobiles produced in North America.[6]
After almost two years, the import tariffs failed to increase capacity utilization in the steel industry to 80 percent. President Trump responded in February 2020 by expanding the scope of covered imports to include $0.7 billion worth of “derivative” articles of steel and aluminum. He also stated in the summer of 2020 that he would reintroduce tariffs on Canadian aluminum, but eventually withdrew the request fearing retaliation.[7]
In April 2022, President Biden reached a deal with the EU and the UK to replace the tariffs with quotas for steel and aluminum, prompting the EU to lift their retaliatory tariffs on U.S. exports. Biden reached a similar deal with Japan as well, although they would still be subject to the aluminum tariffs.[8] No other major changes have been announced since.
The Economic Effects of Tariffs on Steel and Aluminum
President Trump was not the first president to target steel imports. In the late 1970s, the Carter administration imposed “antidumping” or countervailing duties on steel imports from Japan if imports fell below a specified price. Eventually, President Reagan negotiated a quota system through voluntary export restraint agreements with Japan and other trading partners. Research by economists Stefanie Lenway, Randall Morck, and Bernard Yeung found that these trade actions increased rent-seeking by less productive steel firms and reduced R&D spending and innovation.[9]
In 2002, President Bush imposed tariffs on steel ranging from 8 to 30 percent after a Section 201 investigation concluded that current steel imports posed “a substantial threat of serious injury” to the steel industry. The tariffs were scheduled to be in effect for three years, but President Bush rescinded them after two, fearing retaliation from other countries after the WTO ruled that the tariffs violated international commitments.[10]
Nonetheless, even in the brief window that the tariffs were in effect, economist Lydia Cox concluded that they had persistent negative effects in “downstream” industries that use steel as intermediate inputs.[11] Rather than absorbing the tariffs, foreign exporters passed them almost entirely to U.S. firms. For industries that were highly exposed, exports fell sharply during the period the tariffs were in effect and remained depressed even after they were lifted for the next eight years. Given how disruptive tariffs are to trade patterns, even temporary ones can generate lasting effects.[12]
Because there are many more steel-consuming than steel-producing industries in the U.S., the Section 201 tariffs likely lowered manufacturing employment. Economists Joseph Francois and Laura Baughman estimated that the Bush tariffs decreased employment by between 50,000 and 197,000 workers, depending on the definition of steel-consuming industry used.[13]
The U.S. International Trade Commission (USITC) found comparatively smaller effects, estimating a less than 0.01 percent hit to GDP, which implies a smaller employment loss.[14] Nonetheless, the tariffs themselves can be quite onerous for the exposed industries. For example, the USITC found that returns to capital declined by more than $600 million in steel-consuming industries.
Broadly, economists have reached similarly negative conclusions regarding the impacts of the recent Section 232 tariffs on the economy. Lydia Cox and Kadee Russ, using an estimate derived from a Federal Reserve Board paper, calculated that the Section 232 tariffs reduced manufacturing employment by about 75,000 jobs.[15] Kyle Handley and other economists looked at the impacts of the import tariffs on export growth in the U.S. and found that companies exposed to the Section 232 tariffs experienced reduced export growth. This occurred because the cost of their inputs rose due to the tariffs, which hindered firms’ ability to increase their exports. For each 1 percent increase in the tariffs on steel and aluminum, export growth fell by 0.11 percent.[16]
The Peterson Institute for International Economics concluded that the tariffs would only create about 8,700 jobs in the steel industry and would come at a high cost as well. The Section 232 tariffs would raise aggregate income in the steel industry by about $2.4 billion in 2018 but raise costs for steel consumers by about $5.6 billion. This implies a cost of nearly $650,000 for every job created.[17]
The aluminum tariffs in particular have disproportionately harmed certain industries. For example, the beverage industry saw its costs rise by $1.4 billion through early 2022 due to the tariffs, with 92 percent going to U.S. rolling mills, U.S. smelters, and Canadian smelters, and the remainder going to the U.S. Treasury, according to one analysis by the research group HARBOR Aluminum.[18] Ford and General Motors estimated that the tariffs cost them about $1 billion each the first year they were in effect—roughly $700 per vehicle produced.[19]
In many cases, firms may face the tariff-burdened price even if the type of aluminum itself is not covered by Section 232. This occurs because firms that use aluminum as inputs typically buy it in bulk, often scrap or recycled content, based on a specific pricing formula. Although recycled content is supposed to be exempt from the tariffs, aluminum producers charge what is known as the “Midwest Premium” price, a benchmark price that accounts for regional variations in supply and demand.[20]
For example, following the immediate announcement of the tariffs, the Midwest Premium price rose by 11.8 percent, larger than the 10 percent tariff on primary aluminum.[21] While broader supply and demand factors determine the price of aluminum, this provides suggestive evidence that aluminum producers may raise prices in excess of tariffs.
The totality of evidence suggests that the costs of tariffs have largely been borne by U.S. consumers and firms. Federal Reserve Board economist Mary Amiti along with other academics found complete pass-through to these groups the first year the steel tariffs were in effect. In the following years, the pass-through rate fell 50 percent, implying that half of the costs were borne by foreign exporters of steel—mostly the EU, South Korea, and Japan. Although these exporters lowered prices somewhat in response to the tariffs, U.S. firms and consumers still paid higher prices than they would have without the tariffs.[22]
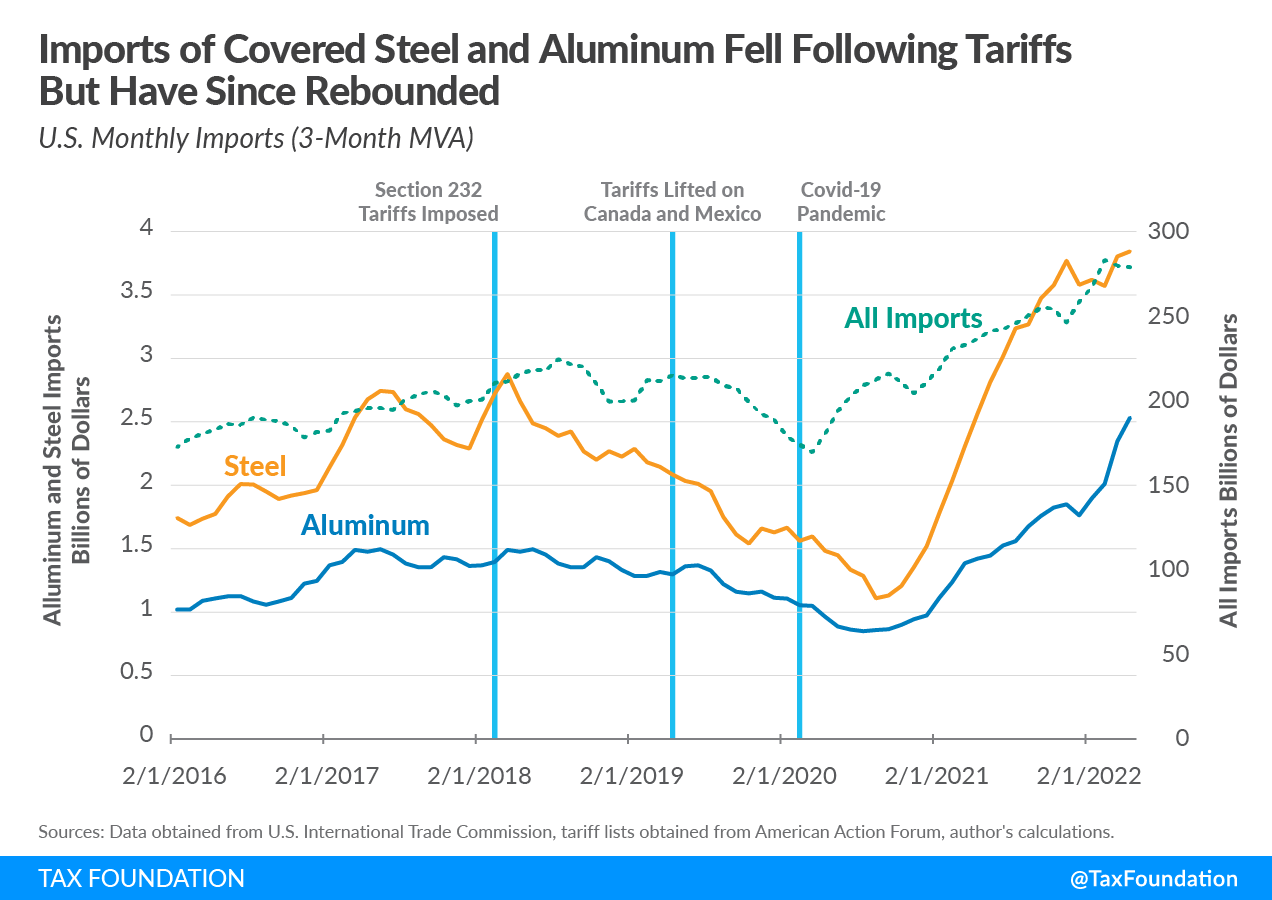
As shown below, the tariffs have led to declines in imports of steel and aluminum. Imports of covered steel declined by 39 percent in the two years following the tariffs, prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, while imports of covered aluminum declined by 24 percent over the same period (Figure 1). Covered steel imports continued to fall until September 2020 but have since recovered significantly, exceeding their previous peak in April 2018. Notably, imports of covered steel rose much more rapidly than overall U.S. imports, which exhibited a similar upward trajectory over this period. Covered aluminum imports began rising sharply in early 2021 after bottoming out in August 2020 and have continued to increase since.
However, a closer look reveals that this apparent recovery in imports may be driven by different factors. For example, the prices of covered aluminum imports have risen faster than the quantities. Since August 2020, imported quantities of covered aluminum have risen 57 percent, while the prices have risen nearly 90 percent. For steel, both quantities and prices have seen explosive growth since September 2020, rising by 104 percent and 69 percent, respectively. Much of this price growth is likely attributable to COVID-related supply constraints and fiscal and monetary stimulus, the latter of which increased aggregate demand and drove consumption of imports higher.[23]
Currently, just over half of all aluminum used in production is imported, according to one estimate for HARBOR Aluminum.[24] And around 78 percent of all steel is imported.[25] As imports constitute a significant share of steel and aluminum used in production, tariffs can have notable impacts on producer prices in manufacturing. Looking at the industry level, the tariffs immediately increased producer prices at the foundries and refineries. The primary metals and fabricated metals industries saw their prices increase by 6 percent and 4 percent, respectively, one year after the tariffs were imposed.[26] As noted earlier, based on research studying export growth in steel- and aluminum-consuming industries, these costs were eventually passed onto other consumers through higher prices, ultimately reducing their exports.
Modeling the Revenue and Economic Impacts of Repealing the Section 232 Tariffs
Currently, $2.9 billion worth of tariffs remain on steel and aluminum, down from about $5 billion when the tariffs were first imposed in 2018. Changes to tariff policy have likely somewhat dampened the negative effects. Exempting Canada—the largest exporter of aluminum to the U.S.—from the tariffs may have mitigated some of the harmful impacts, although as noted earlier purchasers of aluminum are still generally paying tariff-burdened prices. Similarly, President Biden exempting the EU—the largest exporter of steel to the U.S.—from the tariffs likely further reduced the harm.[27] Nonetheless, a significant share of U.S. imports of steel and aluminum are still subject to the tariffs, and even temporary tariffs can have persistent effects, as explained earlier.
We estimate that repealing these tariffs would boost long-run GDP by 0.02 percent and create about 4,000 jobs. Notably, our GDP estimates are comparable to the USITC’s original estimate for the Bush steel tariffs. Government revenues per year would decline by $2.4 billion, slightly less than the $2.9 billion currently raised through the tariffs due to the increased income and payroll tax revenue from the boost to GDP.
| Long Run GDP | +0.02% |
| GDP (billions of dollars) | +3.3 |
| Change in Revenue per year (billions of dollars) | -$2.4 |
| Wages | +0.01% |
| FTE Jobs | +4,000 |
| Source: Tax Foundation General Equilibrium Model, September 2022. | |
Our estimates should be considered a lower bound of the positive impacts, as we do not consider the effects of repealing the remaining non-tariff barriers such as the tariff-rate quotas (TRQs) on steel and aluminum for certain countries. Nor do we consider the impacts of countries repealing their $1.6 billion in retaliatory tariffs on U.S. exports, which would likely further increase GDP.[28]
Conclusion
Although the tariffs were enacted to address national security concerns, they have had negative unintended consequences on American industries and consumers. While steel- and aluminum-producing industries may have experienced a short-run boost in employment due to the tariffs, these came at a high cost to purchasers of steel and aluminum, with one estimate suggesting a cost of $650,000 per job created in the steel industry. Because tariffs are taxes on imports and raise the cost of production, we estimate that repealing the Section 232 tariffs would strengthen the U.S. economy and create jobs.
[1] Rachel F. Fefer, et al., “Section 232 Investigations: Overview and Issues for Congress,” Congressional Research Service, May 18, 2021, https://crsreports.congress.gov/product/pdf/R/R45249.
[2] Ibid.
[3] Ibid.
[4] Ibid.
[5] Marin Weaver, “Section 232 and 301 Trade Actions in 2018,” U.S. International Trade Commission, accessed September 12, 2022, https://www.usitc.gov/research_and_analysis/trade_shifts_2018/special_topic.htm.
[6] Ibid.
[7] Rachel F. Fefer, et al., “Section 232 Investigations: Overview and Issues for Congress,” Congressional Research Service, May 18, 2021, https://crsreports.congress.gov/product/pdf/R/R45249.
[8] Erica York, “Tracking the Economic Impact of U.S. Tariffs and Retaliatory Actions,” Tax Foundation, April 1, 2022, https://taxfoundation.org/tariffs-trump-trade-war/.
[9] Stefanie Lenway, Randall Morck, and Bernard Yeung, “Rent Seeking, Protectionism, and Innovation in the American Steel Industry,” The Economic Journal 106:435 (March 1996): 410-421, https://pages.stern.nyu.edu/~byeung/rentseeking.pdf.
[10] Lydia Cox, “The Long-Term Impact of Steel Tariffs on U.S. Manufacturing,” Harvard University Department of Economics (Nov. 7, 2021), https://scholar.harvard.edu/files/lydiacox/files/cox_steel_tariffs_jmp.pdf.
[11] Ibid.
[12] Ibid.
[13] Joseph Francois and Laura M. Baughman, “The Unintended Consequences of U.S. Steel Import Tariffs: A Quantification of the Impact During 2002,” Trade Partnership Worldwide, LLC (Feb. 4, 2003), https://tradepartnership.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/06/2002jobstudy.pdf.
[14] Bonnie J. Noreen, et al., “Steel-Consuming Industries: Competitive Condition with Respect to Steel Safeguard Measures,” U.S. International Trade Commission (September 2003), https://www.usitc.gov/publications/safeguards/3632/pub3632_vol3_all.pdf.
[15] Kadee Russ and Lydia Cox, “Steel Tariffs and U.S. Jobs Revisited,” EconoFact, Feb. 6, 2020, https://econofact.org/steel-tariffs-and-u-s-jobs-revisited.
[16] Kyle Handley, Fariha Kamal, and Ryan Monarch, “Rising Import Tariffs, Falling Export Growth: When Modern Supply Chains Meet Old-Style Protectionism,” National Bureau of Economic Research, Working Paper 26611 (August 2020), https://www.nber.org/papers/w26611.
[17] Gary Clyde Hufbauer and Euijin Jung, “Steel Profits Gain, but Steel Users Pay, under Trump’s Protectionism,” Peterson Institute for International Economics, Dec. 20, 2018, https://www.piie.com/blogs/trade-and-investment-policy-watch/steel-profits-gain-steel-users-pay-under-trumps.
[18] Beer Institute, “New Research Shows the Tariffs on Aluminum Have Cost the U.S. Beverage Industry $1.4 Billion,” April 4, 2022, https://www.beerinstitute.org/press-releases/new-research-shows-the-tariffs-on-aluminum-have-cost-the-u-s-beverage-industry-1-4-billion/.
[19] Michael Schultz et al., “U.S. Consumer & Economic Impacts of U.S. Automotive Trade Policies,” Center for Automotive Research, February 2019, https://www.cargroup.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/US-Consumer-Economic-Impacts-of-US-Automotive-Trade-Policies-.pdf.
[20] S&P Global, “Platts Aluminum Midwest Premium Explained,” accessed Sept. 12, 2022, https://www.spglobal.com/en/perspectives/platts-aluminum-midwest-premium-explained.
[21] Douglas Holtx-Eakin and Jacqueline Varas, “Do Tariffs Impact Aluminum Prices? The Case of Aluminum,” American Action Forum, Jan 28, 2020, https://www.americanactionforum.org/research/do-tariffs-impact-prices-the-case-of-aluminum/.
[22] Mary Amiti, Stephen J. Redding, and David E. Weinstein, “Who’s Paying for the U.S. Tariffs? A Longer-Term Perspective,” American Economic Association Papers and Proceedings 110 (May 2020): 541–546, http://www.princeton.edu/~reddings/pubpapers/ARW-May-2020.pdf.
[23] “CPI for All Urban Consumers,” Bureau of Labor Statistics, accessed Sep 12, 2022, https://www.bls.gov/cpi/.
[24] Kust Desai, “Fact Check: Does the U.S. Import 90% of its Aluminum?,” CheckYourFact, Mar. 8, 2018, https://checkyourfact.com/2018/03/08/fact-check-us-imports-90-percent-aluminum/.
[25] Meghan Keneally, “Key Facts about the U.S. Steel and Aluminum Industries,” ABC News, Mar. 8, 2018, https://abcnews.go.com/Business/key-facts-us-steel-aluminum-industries/story?id=53616380.
[26] International Trade Administration, “ITA Manufacturing Industry Tracker,” accessed Sep 12, 2022, https://www.trade.gov/data-visualization/ita-manufacturing-industry-tracker
[27] Mary Amiti, Sebastian Heise, and Noah Kwicklis, “Will New Steel Tariffs Protect U.S. Jobs?,” Liberty Street Economics, April 19, 2018, https://libertystreeteconomics.newyorkfed.org/2018/04/will-new-steel-tariffs-protect-us-jobs/.
[29] Erica York, “Tracking the Economic Impact of U.S. Tariffs and Retaliatory Actions,” Tax Foundation, April 1, 2022, https://taxfoundation.org/tariffs-trump-trade-war/.